Stupid Question 232-233: What are environment variables, and do I set and use environment variables in Command Prompt and PowerShell?
If you want to save the path of an executable to a permanent variable you can do so from Command Prompt or PowerShell. Setting one in Command Prompt does not set it in PowerShell. Environment variables are values stored in an object (and can be changed) and these are stored in the registry.(Stupid Question 114: What is the “Windows Registry”?).
[caption id=“attachment_7312” align=“aligncenter” width=“695”]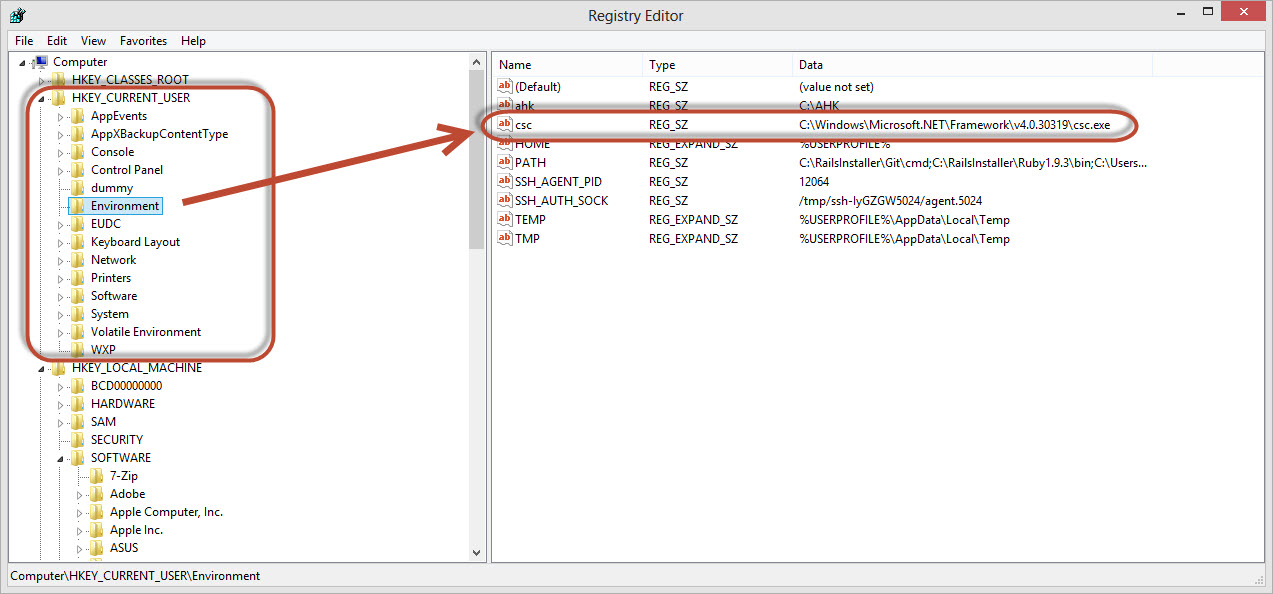
The syntax for setting one temporarily is by using
set variableName C:\mypath\myExecutable.exe
To set it permanently use
setx variableName C:\mypath\myExecutable.exe
To read the contents:
echo %variableName%
To invoke/use variable:
%variableName%
In PowerShell they are set the same way,
Setx variableName C:\mypath\myExecutable.exe
But you read it by using:
gi env:variableName
And invoke/use by:
& $env:variableName
Give it a go with the C# compiler, by using (this is the path for me on my Windows 8 computer for the csc.exe) in PowerShell:
setx csc C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\csc.exe
Then compile a .cs file like so:
C:\Temp\ & $env:csc test.cs
This outputstest.exe
If you prefer clicking on buttons you can set variables in Advanced System Settings:
[caption id=“attachment_7302” align=“aligncenter” width=“695”]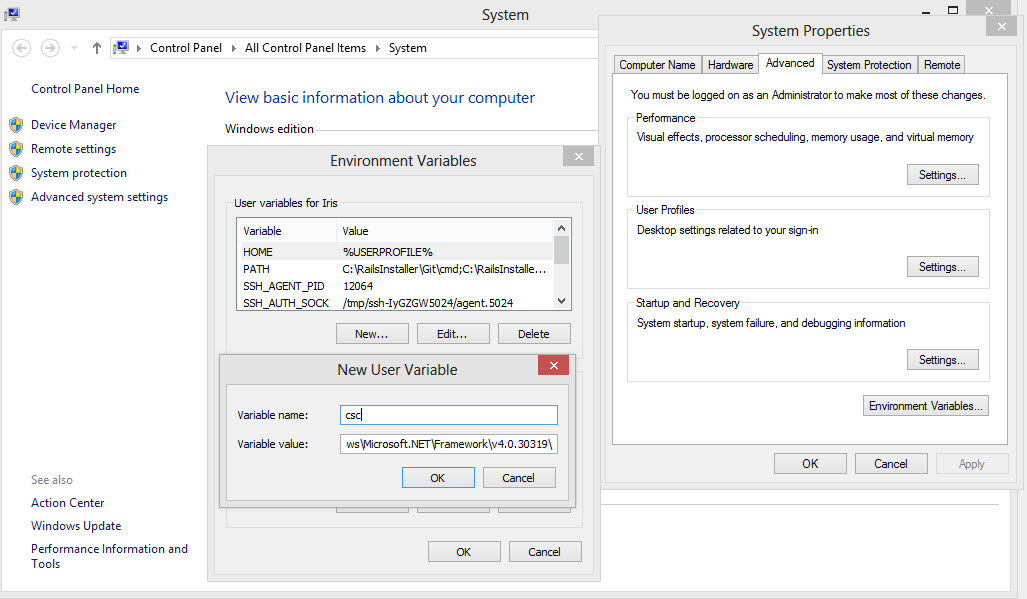
Comments
Last modified on 2013-08-21
